[cs_content][cs_section parallax=”false” separator_top_type=”none” separator_top_height=”50px” separator_top_angle_point=”50″ separator_bottom_type=”none” separator_bottom_height=”50px” separator_bottom_angle_point=”50″ style=”margin: 0px;padding: 45px 0px;”][cs_row inner_container=”true” marginless_columns=”false” style=”margin: 0px auto;padding: 0px;”][cs_column fade=”false” fade_animation=”in” fade_animation_offset=”45px” fade_duration=”750″ type=”1/1″ style=”padding: 0px;”][cs_text]Forensic Chemistry > 2. Analysis of organic material can distinguish plant and animal material > Distinguishing Between Plant And Animal Carbohydrates’ Composition >[/cs_text][cs_text style=”color: #800000;font-family: “Oxygen”,sans-serif;”]Distinguish between plant and animal carbohydrates’ composition in terms of the presence of Cellulose, Starch, Glycogen[/cs_text][cs_text]Cellulose
– works for structural support
– consists of repeating units of glucose linked by β-1,4 glycosidic bonds
– structural component of cell walls in plants[/cs_text][cs_text]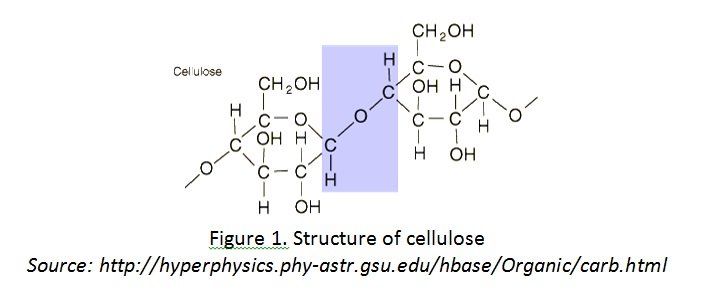 [/cs_text][cs_text]Starch
[/cs_text][cs_text]Starch
– energy storage in plants
– source of energy for animals
– consists of repeating units of glucose which has two types:
- Amylose (about 20%)
– linear polymer joined by α-1,4 glycosidic bonds[/cs_text][cs_text]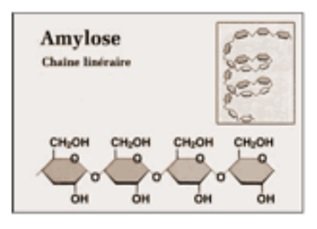 [/cs_text][cs_text] 2. Amylopectin (about 80%)
[/cs_text][cs_text] 2. Amylopectin (about 80%)
– branched polymer joined by α-1,4 and α-1,6 glycosidic bonds[/cs_text][cs_text]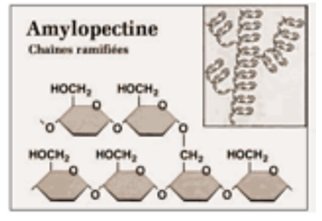 [/cs_text][cs_text]Glycogen
[/cs_text][cs_text]Glycogen
– branched repeating units of glucose
– has similarities in properties and functions of starch
– energy storage in animals
– mostly found in liver and muscles
– synthesized by animals from glucose which served as a short term energy storage[/cs_text][cs_text]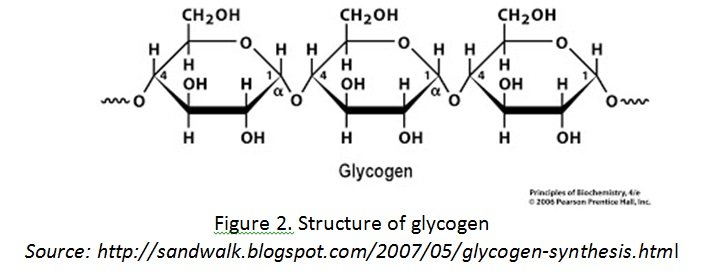 [/cs_text][/cs_column][/cs_row][/cs_section][/cs_content]
[/cs_text][/cs_column][/cs_row][/cs_section][/cs_content]