Forensic Chemistry > 4. DNA is an important compound found in all living things and is a most useful identification molecule > The Structure And Composition of DNA >
Outline the structure and composition of DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
- A form of nucleic acid which are made up of its building blocks called nucleotides covalently linked together by 3’,5’- phosphodiester linkages
- In DNA, the nucleotides are composed of an aldopentose (2-deoxyribose) bonded to a phosphate group and linked to a heterocyclic purine and pyrimidine bases (nitrogenous bases)
Purine:
- Adenine (A)
- Guanine (G)
Pyrimidine:
- Cytosine (C)
- Thymine (T)

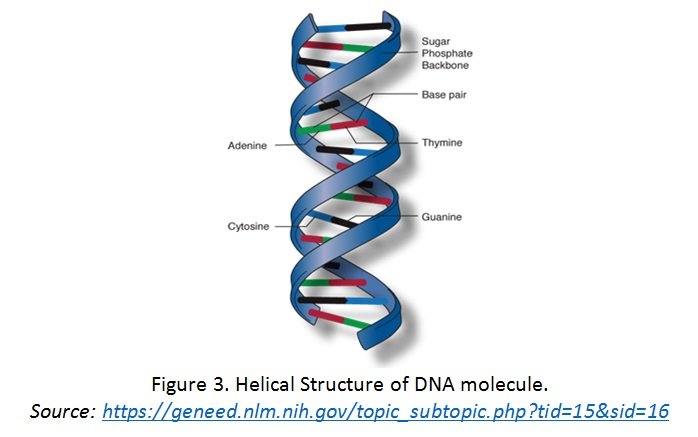
Structure of DNA
- Primary Structure
- consist of alternating sugar-phosphate backbone with different nitrogenous bases attached onto it
- Its individual nucleotides are connected via a phosphate ester linkage between the 5’-phosphate group on one nucleotide residue and the 3’-hydroxyl on the sugar of another nucleotide residue
- Primary Structure

- Secondary Structure
- consist of two polynucleotide strands coiled around each other in a double helix
- The two antiparallel strands which are held together by hydrogen bonds pairs are complementary due to specific base pairing
- Secondary Structure
Chargaff’s rule
- %A = %T
- %C = %G