Industrial Chemistry > 1. Industrial chemistry processes have enabled scientists to develop replacements for natural products > The Issues Associated With Shrinking World Resources >
Discuss the issues associated with shrinking world resources with regard to one identified natural product that is not a fossil fuel, identifying the replacement materials used and/or current research in place to find a replacement for the named material
A. Rubbers
Rubbers (in general)
- used in belting, footwear, hoses, insulators, textile, tubing, tyres and valves due to its elasticity, toughness, impermeability, adhesiveness and insulator-effect.
Natural Rubbers
- polymer of isoprene (polyisoprene) which can be suitably harvested from the sap of rubber trees (usually after 6-7 years)
- undergoes thorough process to come up with desired flexibility and solidity
- utilized for military vehicle tyres in relation to World War II (WWII) and also as components of automobile
Synthetic Rubbers
- synthetic polymers used as substitute for natural rubbers
- cheap, easily manufactured and long-lasting compared to traditional rubber tires
- covered almost 80% of world’s rubber production
- Examples include:
- Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) (most common)

- Polychloroprene or neoprene

- Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) (most common)
Key issues on replacement of natural rubbers to synthetic rubbers
- High demand of natural rubbers for war-related and automobile related needs
- Depletion of natural source of rubbers
- Natural rubbers are more expensive compared to synthetic types due to its significant depletion through time
- Synthetic types are more available and of great quality since its production is not fairly affected by external factors such as weather
Current Research on Development of Synthetic Rubbers
The focus of current development of synthetic rubbers are on inclusion of other materials to
attain:
- ozone, deterioration, corrosion, oil and heat resistance
- Light stability
- Low gas permeability
- Environment-friendly rubbers
B. Guano
Guano (Dung)
- Is a bat and bird droppings
- Non-renewable resource which were widely used for production of nitrates
- Used as suitable fertilizer for plants and lawns
- Also used as natural fungicide in the soil
Synthetic Nitrates
- Laboratory-made nitrates that are currently and widely used as main component of fertilizers
- Can be produced from tandem processes, namely Haber-Bosch and Ostwald processes.
Key issues on replacement of guano (as source of nitrates) to synthetic nitrates production
- Great demand for nitrates as component of fertilizers to boost agriculture as a consequence of increasing population in the early 1900s
- High demand for nitrates as component of explosives for World War I (WWI), leading to search for an alternative source
- Natural nitrates are not readily available and easily accessible since guano is a nonrenewable resource, taking long period of time to generate sufficient amount of nitrates
- The Haber-Bosch process was developed to produce ammonia from Nitrogen and Hydrogen which can be subjected to Ostwald process to produce nitrates in enough period of time, making it more available in comparison to nitrates from Guano
- The Haber process is cheap and efficient in producing ammonia, implying the production of nitrates to be cheap and of high quality Current Research on Development of Synthetic Nitrates
Haber-Bosch Process
industrial process for producing ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen
- Catalyst: Iron
- Condition: High Temperature and Pressure

Ostwald Process
- Ammonia is reacted with oxygen to form nitric acid
NH3 + 2O2 -> HNO3 + H2O
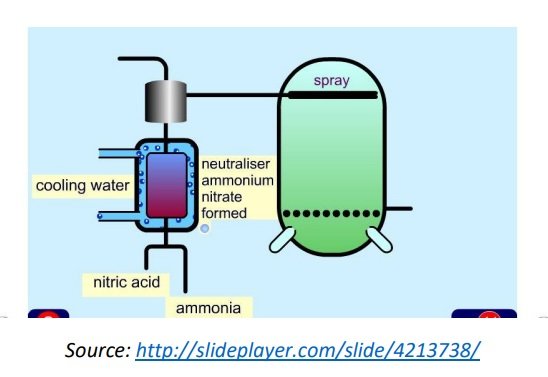
Ammonium Nitrate Production
- The nitric acid is then reacted with more ammonia to yield ammonium nitrate (in solid
form)
HNO3 + NH3 -> NH4NO3