[cs_content][cs_section parallax=”false” separator_top_type=”none” separator_top_height=”50px” separator_top_angle_point=”50″ separator_bottom_type=”none” separator_bottom_height=”50px” separator_bottom_angle_point=”50″ style=”margin: 0px;padding: 45px 0px;”][cs_row inner_container=”true” marginless_columns=”false” style=”margin: 0px auto;padding: 0px;”][cs_column fade=”false” fade_animation=”in” fade_animation_offset=”45px” fade_duration=”750″ type=”1/1″ style=”padding: 0px;”][cs_text]Industrial Chemistry > 4. The industrial production of sodium hydroxide requires the use of electrolysis > The Difference Between Galvanic Cells And Electrolytic Cells >[/cs_text][cs_text style=”color: #800000;font-family: “Oxygen”,sans-serif;”]Explain the difference between galvanic cells and electrolytic cells in terms of energy requirements[/cs_text][cs_text]GALVANIC CELL
- uses a spontaneous reaction in order to generate electricity
- composed of two half-cells with separate electrolytes and a salt bridge connecting the electrolyte solutions
- electrons are lost from the anode and travel through a conductive wire (electric current) where it is absorbed by cathode and reduction takes place
ELECTROLYTIC CELL
- electrical energy is required in order for a non-spontaneous chemical reaction to occur
- composed of two electrodes placed in the same electrolyte solution
- electrons are withdrawn from the anode by the battery and then flows from the negative terminal of the battery to the cathode
- amount of reactants consumed or products formed depends on the amount of electricity transferred at the electrodes
Comparing galvanic and electrolytic cells: [/cs_text][cs_text] [/cs_text][cs_text]
[/cs_text][cs_text]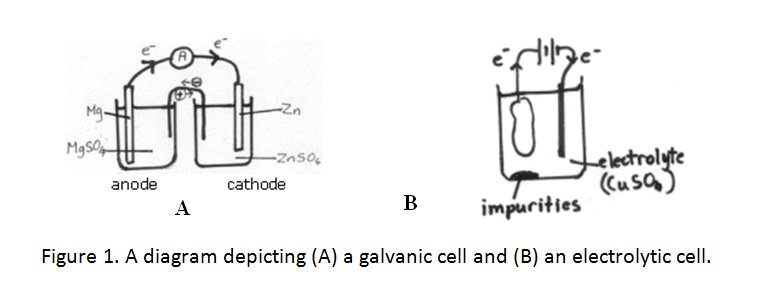 [/cs_text][/cs_column][/cs_row][/cs_section][/cs_content]
[/cs_text][/cs_column][/cs_row][/cs_section][/cs_content]