Industrial Chemistry > 4. The industrial production of sodium hydroxide requires the use of electrolysis > The Different Products of The Electrolysis of Aqueous And Molten Sodium Chloride >
Analyse information from secondary sources to predict and explain the different products of the electrolysis of aqueous and molten sodium chloride
ELECTROLYSIS OF MOLTEN NaCl
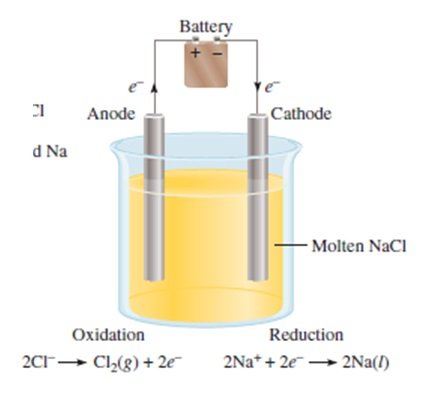
- only sodium and chloride ions present
- the products formed are chlorine gas and sodium metal
- only possible reaction at the anode is the oxidation of chloride ions to form chlorine gas:
2Cl– (l) à Cl2 (g) + 2e–
- only possible reaction at the cathode is the reduction of sodium ions to form sodium metal:
2Na+ (l) + 2e–à 2Na (l)
Full Equation:
2NaCl (l) à Cl2 (g) + 2Na (l)
ELECTROLYSIS OF AQUEOUS NaCl
- complication is resulted by the presence of water
- possible anode reactions are oxidation of chloride ions to form chlorine gas and oxidation of water molecules to form H+ and oxygen gas
- If oxidation of chloride ions happened at anode:
2Cl– (l) à Cl2 (g) + 2e– E = -1.36 V
- If oxidation of water molecules happened at anode:
2H2O (l)à O2 (g) + 4H+ (aq) + 4e– E = -1.23 V
- possible cathode reactions are reduction of sodium ions to form sodium metaland reduction of water molecules to form hydroxide and hydrogen gas
- If reduction of sodium ions happened at cathode:
- possible cathode reactions are reduction of sodium ions to form sodium metaland reduction of water molecules to form hydroxide and hydrogen gas
Na+ (aq) + e–à Na (s) E = -2.71 V
- If reduction of water molecules happened at cathode:
2H2O (l) + 2e–à 2OH– (aq) + H2 (g) E = -0.83 V
- the products formed are hydroxide ions and chlorine and hydrogen gases
Reduction Process
- The reaction with higher EMF is most likely to proceed as it will lead to more spontaneity
Oxidation Process
- theoretically, oxidation of water is expected to happen at the anode given that it is more spontaneous than the oxidation of chloride ions
- however, oxidation of water molecules happens only when a dilute solution of NaCl undergoes electrolysis
- in electrolytic process, the voltage required for some reactions is considerably higher than what the electrode potential indicates
- Overvoltage – difference between the electrode potential and the actual voltage required to cause electrolysis
- the overvoltage for O2 formation is quite high which allows formation of Cl2 for electrolysis of concentrated NaCl
- in addition, the conditions are different to those in which standard reduction potentials are measured,g. concentrations of Cl– ions is high, not 1 molL-1
Full Equation:
2NaCl (aq) + 2H2O (l) à 2NaOH (aq) + Cl2 (g) + H2 (g)
