[cs_content][cs_section parallax=”false” separator_top_type=”none” separator_top_height=”50px” separator_top_angle_point=”50″ separator_bottom_type=”none” separator_bottom_height=”50px” separator_bottom_angle_point=”50″ style=”margin: 0px;padding: 45px 0px 0px;”][cs_row inner_container=”true” marginless_columns=”false” style=”margin: 0px auto;padding: 0px;”][cs_column fade=”false” fade_animation=”in” fade_animation_offset=”45px” fade_duration=”750″ type=”1/1″ style=”padding: 0px;”][cs_text]Monitoring and Management > 4. The Atmosphere >
Describe the composition and layered structure of the atmosphere[/cs_text][/cs_column][/cs_row][/cs_section][cs_section parallax=”false” separator_top_type=”none” separator_top_height=”50px” separator_top_angle_point=”50″ separator_bottom_type=”none” separator_bottom_height=”50px” separator_bottom_angle_point=”50″ style=”margin: 0px;padding: 45px 0px;”][cs_row inner_container=”true” marginless_columns=”false” style=”margin: 0px auto;padding: 0px;”][cs_column fade=”false” fade_animation=”in” fade_animation_offset=”45px” fade_duration=”750″ type=”1/3″ style=”padding: 0px;”][cs_text]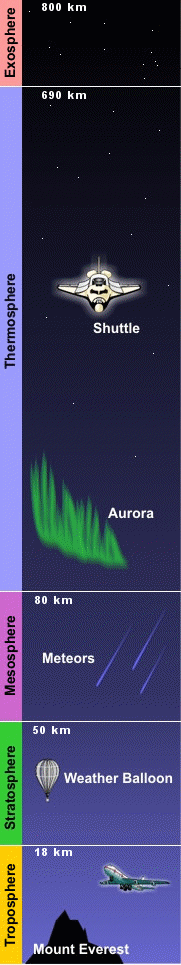
[/cs_text][/cs_column][cs_column fade=”false” fade_animation=”in” fade_animation_offset=”45px” fade_duration=”750″ type=”2/3″ style=”padding: 0px;”][cs_text]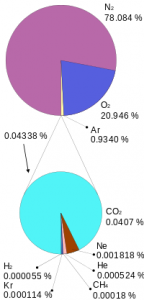
- Atmosphere: The gaseous mixture surrounding the surface of the Earth.
- The dry atmosphere is composed of the following gases:
| Gas | % by volume |
| Nitrogen | 78.08 |
| Oxygen | 20.95 |
| Argon | 0.93 |
| Carbon dioxide | 0.036 |
| Other | 0.004 |
- The dried atmospheric composition varies little with altitude.
- The percentage of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere has been increasing over the last 150 years, largely due to the burning of fossil fuels.
- The percentage of water vapour in the atmosphere varies considerable, particularly in the troposphere, where it ranges from 0.5 % to 5 %.
- The atmosphere consists of a series of layers, the boundaries between which are defined by marked changes in the rate of change of temperature.
| Layer | Extent (Altitude) |
Features |
| Troposphere | Earth’s surface to ~15 km | Temperature decreases with altitude |
| Stratosphere | ~15 km to ~50 km | • Temperature increases with altitude • Contains ozone layer, with maximum concentration at altitude of ~25 km |
| Mesosphere | ~50 km to ~85 km | Temperature decreases with altitude |
| Thermosphere | ~85km to ~500 km | Temperature increases with altitude |
| Exosphere | ~500 km outwards | • Particles can overcome the Earth’s gravity an escape into space • Diffuses into space |
| Ionosphere | ~60 km outwards | • Incorporates the thermosphere and part of the mesosphere • Contains free ions, atoms and electrons |
[/cs_text][/cs_column][/cs_row][/cs_section][cs_section parallax=”false” separator_top_type=”none” separator_top_height=”50px” separator_top_angle_point=”50″ separator_bottom_type=”none” separator_bottom_height=”50px” separator_bottom_angle_point=”50″ style=”margin: 0px;padding: 45px 0px;”][cs_row inner_container=”true” marginless_columns=”false” style=”margin: 0px auto;padding: 0px;”][cs_column fade=”false” fade_animation=”in” fade_animation_offset=”45px” fade_duration=”750″ type=”1/1″ style=”padding: 0px;”][x_video_embed no_container=”false” type=”16:9″][/x_video_embed][/cs_column][/cs_row][/cs_section][/cs_content]