Polyethylene (PE)
Structure
- Composed of several non-polar, saturated monomers of ethylene molecules.
- Forms a long of chain of hydrogen atoms connected to a carbon backbone.
Reference image for structure:

Properties
- Resistant to strong acids, bases, gentle oxidants and reducing agents.
- Dissolve in aromatic hydrocarbons and chlorinated solvents in high temperature.
- Good electrical insulator.
Uses
- For packaging of goods in a variant number of industries.
- As a consumer good for disposing trash and garbage.
- For manufacture of rope, fishing net and other sport goods.
- For production of pipes and fittings.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Structure
- Vinyl polymer made of a carbon backbone where hydrogens in specific positions are replaced by chlorine atoms.
Reference image for structure:

Properties
- Tough and possesses high mechanical strength.
- Heat stability is quite poor which calls for the addition of heat stabilizers to ensure the product’s properties.
- A good insulator but because of having a high polarity, its insulating properties is less as compared to that of polyethylene and polypropylene.
- Resistant to corrosive materials such as acids, salts, bases, fats, and alcohols.
Uses
- Half of the world’s polyvinyl resin is used for manufacturing municipal and industrial pipes for its ability to resist corrosion.
- Used for creating signs and other forms of commercial signage products.
- Used as insulation on electric cables.
- PVC fabric is water-resistant, used for its weather-resistant qualities in coats, skiing equipment, shoes, jackets, aprons, and sports bags.
Polystyrene (PS)
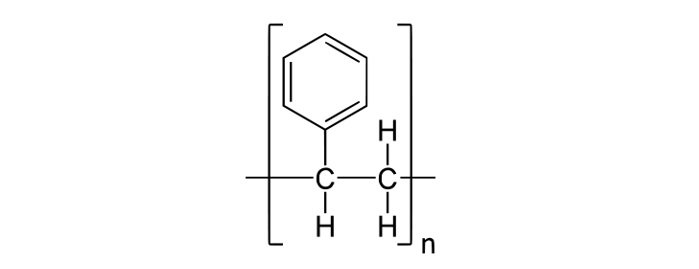
Structure
- Long chain hydrocarbon where phenyl groups are attached to alternating carbon atoms.
Reference image for structure:
Properties
- High tensile strength and can tolerate high impact.
- Malleable and can be moulded into different shapes.
- Recyclable and environment friendly.
- A good heat insulator.
Uses
- Often used to make parts of electronic appliances because it is cheap and chemically inert.
- Used to make automobile parts, including knobs, instrument panels, trim etc.
- Widely used in food storing and packaging.
- Due to its clarity and ease of sterilization, polystyrene is used for a wide range of medical applications, including tissue culture trays, test tubes, petri dishes, diagnostic components, housings for test kits and medical devices.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
Structure
- Synthetic fluoropolymer of tetrafluoroethylene.
Reference image for structure:

Properties
- Highly flexible.
- Resistant to heat, chemical and even water.
- High electrical resistance and dielectric strength.
Uses
- Major application in wiring of aerospace and computer applications.
- Used as non-stick coating for pans and cookwares.
- Due to being resistant to corrosion, it is often used in containers and pipework for corrosive substances.
