[cs_content][cs_section parallax=”false” separator_top_type=”none” separator_top_height=”50px” separator_top_angle_point=”50″ separator_bottom_type=”none” separator_bottom_height=”50px” separator_bottom_angle_point=”50″ style=”margin: 0px;padding: 45px 0px;”][cs_row inner_container=”true” marginless_columns=”false” style=”margin: 0px auto;padding: 0px;”][cs_column fade=”false” fade_animation=”in” fade_animation_offset=”45px” fade_duration=”750″ type=”1/1″ style=”padding: 0px;”][cs_text]
Production of Materials > 2. Biomass Research >
Describe the structure of cellulose and identify it as an example of a condensation polymer found as a major component of biomass[/cs_text][/cs_column][/cs_row][/cs_section][cs_section parallax=”false” separator_top_type=”none” separator_top_height=”50px” separator_top_angle_point=”50″ separator_bottom_type=”none” separator_bottom_height=”50px” separator_bottom_angle_point=”50″ style=”margin: 0px;padding: 45px 0px;”][cs_row inner_container=”true” marginless_columns=”false” style=”margin: 0px auto;padding: 0px;”][cs_column fade=”false” fade_animation=”in” fade_animation_offset=”45px” fade_duration=”750″ type=”1/1″ style=”padding: 0px;”][cs_text]
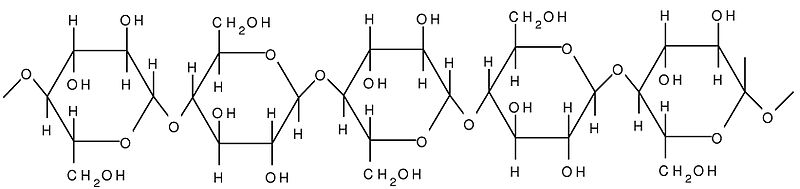
- Cellulose is a polymer that exists in the form of chains made up of many glucose monomers.
- Chains consist of several hundred to several thousand monomers
- The many polar hydroxy groups that exist along cellulose chains form hydrogen bonds with those on adjacent chains.
- The bonding causes bundling of cellulose chains which results in the great length and strength of cellulose fibres.
- The reduced availability of hydroxy groups due to their involvement in hydrogen bonding makes cellulose insoluble and reasonably resistant to chemical attack.
- Biopolymer: A polymer that is made totally or in large part by living organisms.
- Cellulose is a biopolymer, and forms the main structural component of plant cell walls.
- Biomass: Material produced by living organisms.
- Normal dry plant matter (which forms a large proportion of the earth’s biomass) consists of about 50% cellulose, and plants on earth produce approximately 500 billion tonnes of the substance each year.
[/cs_text][/cs_column][/cs_row][/cs_section][cs_section parallax=”false” separator_top_type=”none” separator_top_height=”50px” separator_top_angle_point=”50″ separator_bottom_type=”none” separator_bottom_height=”50px” separator_bottom_angle_point=”50″ style=”margin: 0px;padding: 45px 0px;”][cs_row inner_container=”true” marginless_columns=”false” style=”margin: 0px auto;padding: 0px;”][cs_column fade=”false” fade_animation=”in” fade_animation_offset=”45px” fade_duration=”750″ type=”1/1″ style=”padding: 0px;”][x_video_embed no_container=”false” type=”16:9″][/x_video_embed][/cs_column][/cs_row][/cs_section][/cs_content]