The Acidic Environment > 2. Acidic Oxides >
Calculate volumes of gases given masses of some substances in reactions, and calculate masses of substances given gaseous volumes, in reactions involving gases at 0˚C and 100kPa or 25˚C and 100kPa
- Avogadro’s hypothesis was that equal volumes of gases contain the same number of molecules (at the same temperature and pressure).
- Rearranged, this provides that equal numbers of molecules of different gases occupy the same volume (at the same temperature and pressure).
- Since a mole is a number of molecules, a mole of any gas has the same volume of a mole of any other mass.
- At 0°C and 100 kPa, the molar volume of all gases is 22.71 L.
- At 25°C and 100 kPa, the molar volume of all gases is 24.79 L.
- For example, to determine the volume of hydrogen produced at 0°C an 100 kPa when 2.5 g of sodium reacts with excess water, the following calculations can be performed:
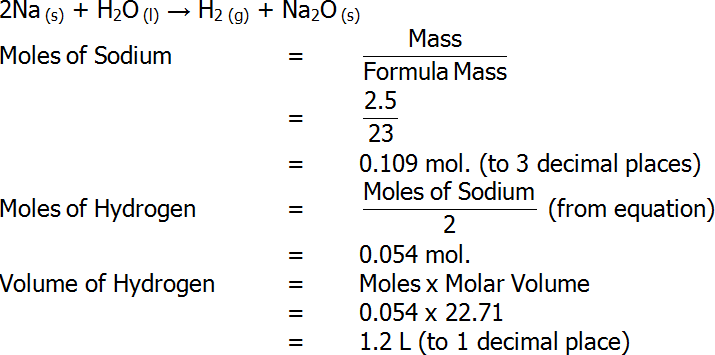
- To determine mass from volume, the above calculations can be performed in reverse.
