[cs_content][cs_section parallax=”false” separator_top_type=”none” separator_top_height=”50px” separator_top_angle_point=”50″ separator_bottom_type=”none” separator_bottom_height=”50px” separator_bottom_angle_point=”50″ style=”margin: 0px;padding: 45px 0px;”][cs_row inner_container=”true” marginless_columns=”false” style=”margin: 0px auto;padding: 0px;”][cs_column fade=”false” fade_animation=”in” fade_animation_offset=”45px” fade_duration=”750″ type=”1/1″ style=”padding: 0px;”][cs_text]Shipwrecks and Salvage > 7. Conservation >
Describe the processes that occur when a saturated solution evaporates and relate this to the potential damage to drying artefacts[/cs_text][/cs_column][/cs_row][/cs_section][cs_section parallax=”false” separator_top_type=”none” separator_top_height=”50px” separator_top_angle_point=”50″ separator_bottom_type=”none” separator_bottom_height=”50px” separator_bottom_angle_point=”50″ style=”margin: 0px;padding: 45px 0px;”][cs_row inner_container=”true” marginless_columns=”false” style=”margin: 0px auto;padding: 0px;”][cs_column fade=”false” fade_animation=”in” fade_animation_offset=”45px” fade_duration=”750″ type=”1/1″ style=”padding: 0px;”][cs_text]
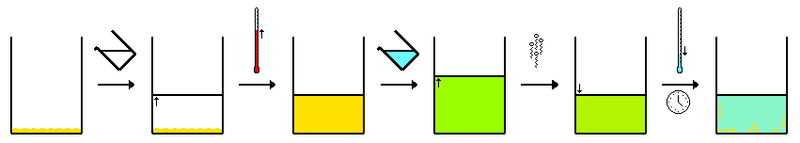
- When a solution of a solid is evaporated, the solution becomes more concentrated until it reaches saturation.
- Saturated Solution: A solution of a substance in which no more of that particular substance can dissolve.
- When a saturated solution is evaporated, the dissolved solid begins to crystallise until only the solid remains.
- When an artefact from a long-submerged wreck is dried, this crystallisation process occurs.
- The formation of salt crystals throughout porous artefacts can cause considerable damage in two main ways:
- Distorting and cracking artefacts.
- Reacting chemically with artefacts.
- Impregnated salts need to be removed from artefacts before they are dried in order to prevent damage.
[/cs_text][/cs_column][/cs_row][/cs_section][/cs_content]