[cs_content][cs_section parallax=”false” separator_top_type=”none” separator_top_height=”50px” separator_top_angle_point=”50″ separator_bottom_type=”none” separator_bottom_height=”50px” separator_bottom_angle_point=”50″ style=”margin: 0px;padding: 45px 0px;”][cs_row inner_container=”true” marginless_columns=”false” style=”margin: 0px auto;padding: 0px;”][cs_column fade=”false” fade_animation=”in” fade_animation_offset=”45px” fade_duration=”750″ type=”1/1″ style=”padding: 0px;”][cs_text]Industrial Chemistry > 5. Saponification is an important organic industrial process > A First Hand Investigation On Saponification > [/cs_text][cs_text style=”color: #800000;font-family: “Oxygen”,sans-serif;”]Perform a first hand investigation to carry out saponification and test the product[/cs_text][cs_text]Experiment: Preparation of Soap
Objective: To prepare soap via saponification and compare its properties with a commercial soap and detergent.
Reagents:
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) pellets
- Coconut oil
- NaCl (solid)
- 1 M NaCl solution
- Distilled water
- Commercial soap and detergent
- Food colouring
Glassware and Equipment:
- 10-mL graduated cylinder
- 100-mL beaker
- Stirring rod
- 6 test tubes
- Bunsen burner
- Tripod + gauze mat + heatproof mat
- Electronic balance
Other Material
- Paper towel
Methodology
Soap Preparation (Saponification)
- Transfer 2-3 spoonfuls NaOH pellets to a 100-mL beaker.
Note:Observe proper lab attire to prevent caustic and corrosive sodium hydroxide from entering eyes and causing irritation and burns.
- Dissolve the NaOH by adding 30 mL distilled water into the beaker
- Add 4 teaspoons of coconut oil
- Gently boil the mixture using Bunsen burner for about 10 minutes with constant stirring
Note: Observe continuous stirring to prevent the occurrence of explosion or solution spitting vigorously causing burns to skin and eyes
- Allow the solution to cool by standing for a few minutes.
- Add 10 g of solid NaCl (measured using electronic balance) to the solution and boil for another couple of minutes.
- Add 2-3 drops of food colouring.
- Decant the liquid layer on top of the curds and wash the remaining solid with NaCl solution.
- Tip the solid (soap) onto a paper towel and allow it to dry overnight.
- Keep the soap for the succeeding analysis.
Comparison of prepared soap, commercial soap and detergent
- Transfer half of the soap into test tube 1 and the other into test tube 2.
- Transfer about the same amount of commercial soap into test tubes 3 and 4.
- Transfer about the same amount of detergent into test tubes 5 and 6.
- Add 3 mL of distilled water to test tubes 1, 3 and 6, and add 3mL of hard water to test tubes 2, 4 and 6.
- Shake each test tube vigorously and record observations. Note the height and density of the froth.
[/cs_text][cs_text]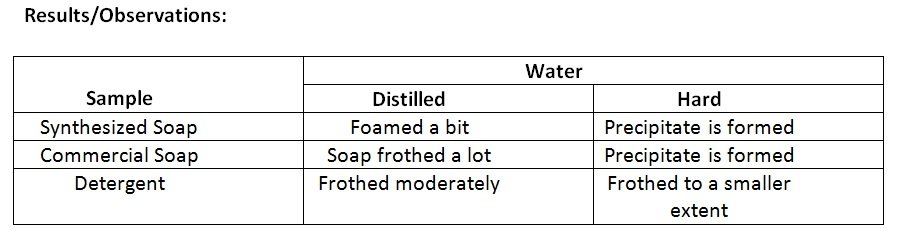 [/cs_text][cs_text]Conclusion:
[/cs_text][cs_text]Conclusion:
- Soap was produced via saponification reaction
- The synthesized soap were found to foam less compared to commercial soap and detergent which can be attributed to its simple composition in comparison to commercial soap and detergent that contain various ingredients
[/cs_text][/cs_column][/cs_row][/cs_section][/cs_content]