[cs_content][cs_section parallax=”false” separator_top_type=”none” separator_top_height=”50px” separator_top_angle_point=”50″ separator_bottom_type=”none” separator_bottom_height=”50px” separator_bottom_angle_point=”50″ style=”margin: 0px;padding: 45px 0px;”][cs_row inner_container=”true” marginless_columns=”false” style=”margin: 0px auto;padding: 0px;”][cs_column fade=”false” fade_animation=”in” fade_animation_offset=”45px” fade_duration=”750″ type=”1/1″ style=”padding: 0px;”][cs_text]Monitoring and Management > 4. The Atmosphere >
Present information from secondary sources to write the equations to show the reactions involving CFCs and ozone to demonstrate the removal of ozone from the atmosphere[/cs_text][/cs_column][/cs_row][/cs_section][cs_section parallax=”false” separator_top_type=”none” separator_top_height=”50px” separator_top_angle_point=”50″ separator_bottom_type=”none” separator_bottom_height=”50px” separator_bottom_angle_point=”50″ style=”margin: 0px;padding: 45px 0px;”][cs_row inner_container=”true” marginless_columns=”false” style=”margin: 0px auto;padding: 0px;”][cs_column fade=”false” fade_animation=”in” fade_animation_offset=”45px” fade_duration=”750″ type=”1/1″ style=”padding: 0px;”][cs_text]
- Ultraviolet radiation causes CFCs to undergo photodissociation, producing highly reactive chlorine free radicals, such as in the case of dichlorodifluoromethane:
- Chlorine free radicals react with ozone, removing it from the atmosphere and producing highly reactive ClO free radicals:
- Due to the continual formation and decomposition of ozone in the stratosphere, oxygen free radicals are present, and these can react with ClO free radicals to reform chlorine free radicals:
- Alternatively, ClO free radicals can undergo photodissociation to reform chlorine free radicals:
- The reformation of chlorine free radicals begins the process again, resulting in a chain reaction.
- One chlorine atom can destroy thousands of ozone molecules in this process, before a reaction with methane, nitrogen dioxide or itself takes place:
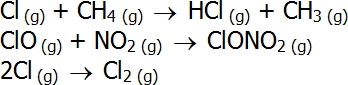
[/cs_text][/cs_column][/cs_row][/cs_section][cs_section parallax=”false” separator_top_type=”none” separator_top_height=”50px” separator_top_angle_point=”50″ separator_bottom_type=”none” separator_bottom_height=”50px” separator_bottom_angle_point=”50″ style=”margin: 0px;padding: 45px 0px;”][cs_row inner_container=”true” marginless_columns=”false” style=”margin: 0px auto;padding: 0px;”][cs_column fade=”false” fade_animation=”in” fade_animation_offset=”45px” fade_duration=”750″ type=”1/1″ style=”padding: 0px;”][x_video_embed no_container=”false” type=”16:9″][/x_video_embed][/cs_column][/cs_row][/cs_section][/cs_content]