[cs_content][cs_section parallax=”false” separator_top_type=”none” separator_top_height=”50px” separator_top_angle_point=”50″ separator_bottom_type=”none” separator_bottom_height=”50px” separator_bottom_angle_point=”50″ style=”margin: 0px;padding: 45px 0px;”][cs_row inner_container=”true” marginless_columns=”false” style=”margin: 0px auto;padding: 0px;”][cs_column fade=”false” fade_animation=”in” fade_animation_offset=”45px” fade_duration=”750″ type=”1/1″ style=”padding: 0px;”][cs_text]Monitoring and Management > 4. The Atmosphere >
Describe ozone as a molecule able to act both as an upper atmosphere UV radiation shield and a lower atmosphere pollutant[/cs_text][/cs_column][/cs_row][/cs_section][cs_section parallax=”false” separator_top_type=”none” separator_top_height=”50px” separator_top_angle_point=”50″ separator_bottom_type=”none” separator_bottom_height=”50px” separator_bottom_angle_point=”50″ style=”margin: 0px;padding: 45px 0px;”][cs_row inner_container=”true” marginless_columns=”false” style=”margin: 0px auto;padding: 0px;”][cs_column fade=”false” fade_animation=”in” fade_animation_offset=”45px” fade_duration=”750″ type=”1/1″ style=”padding: 0px;”][cs_text]
- Ozone is found at very low levels in the lower atmosphere (0.02 ppm in clean air).
- The formation of ozone through the interaction between sunlight, hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxides can lead to higher concentrations in the lower atmosphere or troposphere.
- Ozone is poisonous to humans (as well as most other organisms), with its effects in larger than normal concentrations including:
- Breathing problems.
- Aggravation of respiratory problems.
- Headaches.
- Fatigue.
- Death (in high concentrations).
- Ozone exists at much higher levels in the upper atmosphere or stratosphere (ranging from 2 ppm to 8 ppm in the stratosphere), where 90% of the atmosphere’s oxygen is found.
- In the upper atmosphere both oxygen gas and ozone gas absorb different parts of the ultraviolet radiation range in a cycle of ozone formation and decomposition:
-
- Oxygen absorbs high energy ultraviolet radiation as part of the ozone formation process:
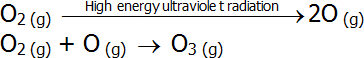
-
- Ozone absorbs medium energy ultraviolet radiation as part of the ozone decomposition process:
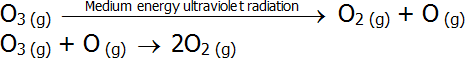
-
- In both of these sets of reactions, the second reaction is exothermic, which accounts for the increasing temperature in the stratosphere.
- Thus, the ozone layer acts as a radiation shield in the upper atmosphere by absorbing medium and high energy ultraviolet radiation.
[/cs_text][/cs_column][/cs_row][/cs_section][cs_section parallax=”false” separator_top_type=”none” separator_top_height=”50px” separator_top_angle_point=”50″ separator_bottom_type=”none” separator_bottom_height=”50px” separator_bottom_angle_point=”50″ style=”margin: 0px;padding: 45px 0px;”][cs_row inner_container=”true” marginless_columns=”false” style=”margin: 0px auto;padding: 0px;”][cs_column fade=”false” fade_animation=”in” fade_animation_offset=”45px” fade_duration=”750″ type=”1/1″ style=”padding: 0px;”][x_video_embed no_container=”false” type=”16:9″][/x_video_embed][/cs_column][/cs_row][/cs_section][/cs_content]



